CASE STUDY: Longitudinal Monitoring for the Emergence of EGFR C797S resistance mutations in NSCLC using blood-based Droplet Digital PCR
Bowling et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2019;2:912-6 DOI: 10.20517/cdr.2019.02 https://cdrjournal.com/article/view/3197
Patient Clinical Background: In October 2014, a never-smoker female presented with new-onset seizures and was diagnosed with an extensive brain and bony metastatic TTF-1 positive lung adenocarcinoma. Tissue EGFR exon 19 deletion (del19) was identified. After an excellent initial response to whole-brain radiation therapy and ongoing erlotinib, she was switched to osimertinib when T790M resistance emerged in July 2016. Molecular testing was conducted using the validated GeneStrat ddPCR platform (Biodesix, Inc., Boulder, Colorado USA) for EGFR L858R, del19 (E746-A750), and T790M [1]. By January 2018 (osimertinib day 540) the patient had discontinued therapy due to resistance and disease progression. She died in hospice care at age 46.
Methods: We used a newly developed ddPCR assay to retrospectively evaluate the emergence of the C797S mutation in six remnant plasma samples from this patient. All Biodesix personnel were blinded to patient case information. The C797S mutation was undetectable on treatment days 0 and 42 but was detectable by day 287. Orthogonal testing with next-generation sequencing showed that only the C797S variant (G>C) was present in circulation. The EGFR del19 and T790M mutations both declined after initial osimertinib treatment but re-emerged by day 287 [Figure 1].
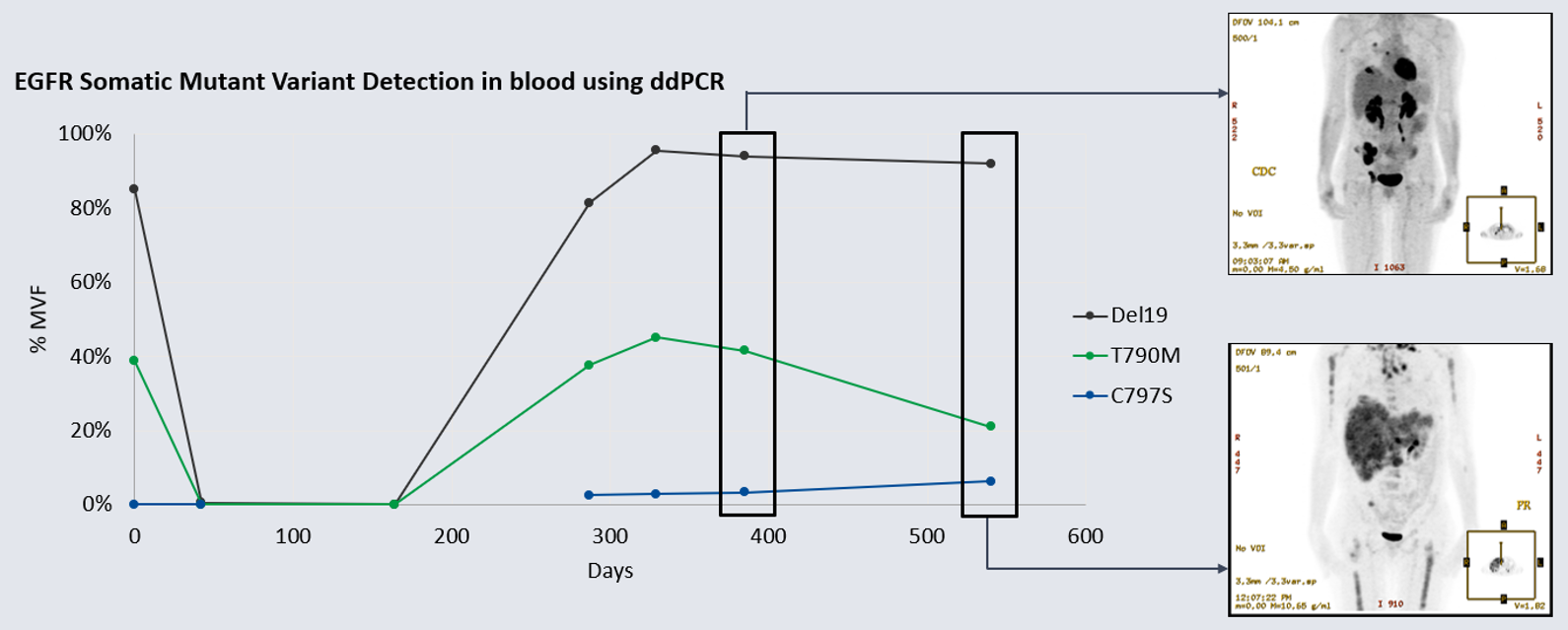
Figure 1: Detection of del19 driver and T790M TKI resistance mutations compared to C797S osimertinib resistance mutation (%MVF) over 540-day osimertinib treatment cycle. Note the day-164 specimen was unavailable for testing for C797S because the sample was exhausted. Insets: patient PET-CT scan on days 385 and 540 (showing disease progression). EGFR: epidermal growth factor; %MVF: percent minor variant frequency; TKI: tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Discussion: Please reference the peer-reviewed case report to learn more!
References:
- Mellert H, Foreman T, Jackson L, Maar D, Thurston S, et al. Development and clinical utility of a blood-based test service for the rapid identification of actionable mutations in non-small cell lung carcinoma. J Mol Diagn 2017;19:404-16.




